In 1893, the legendary scientist Nikola Tesla first transmitted electricity over a distance in a non-contact way at the Chicago World’s Fair. A year later, he lit a phosphor incandescent lamp in the laboratory without any wires. Just over a hundred years have passed since then, and the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction has been used to create wireless charging. What is it, where, how, why? Let’s go figure it out.
What is wireless charging?
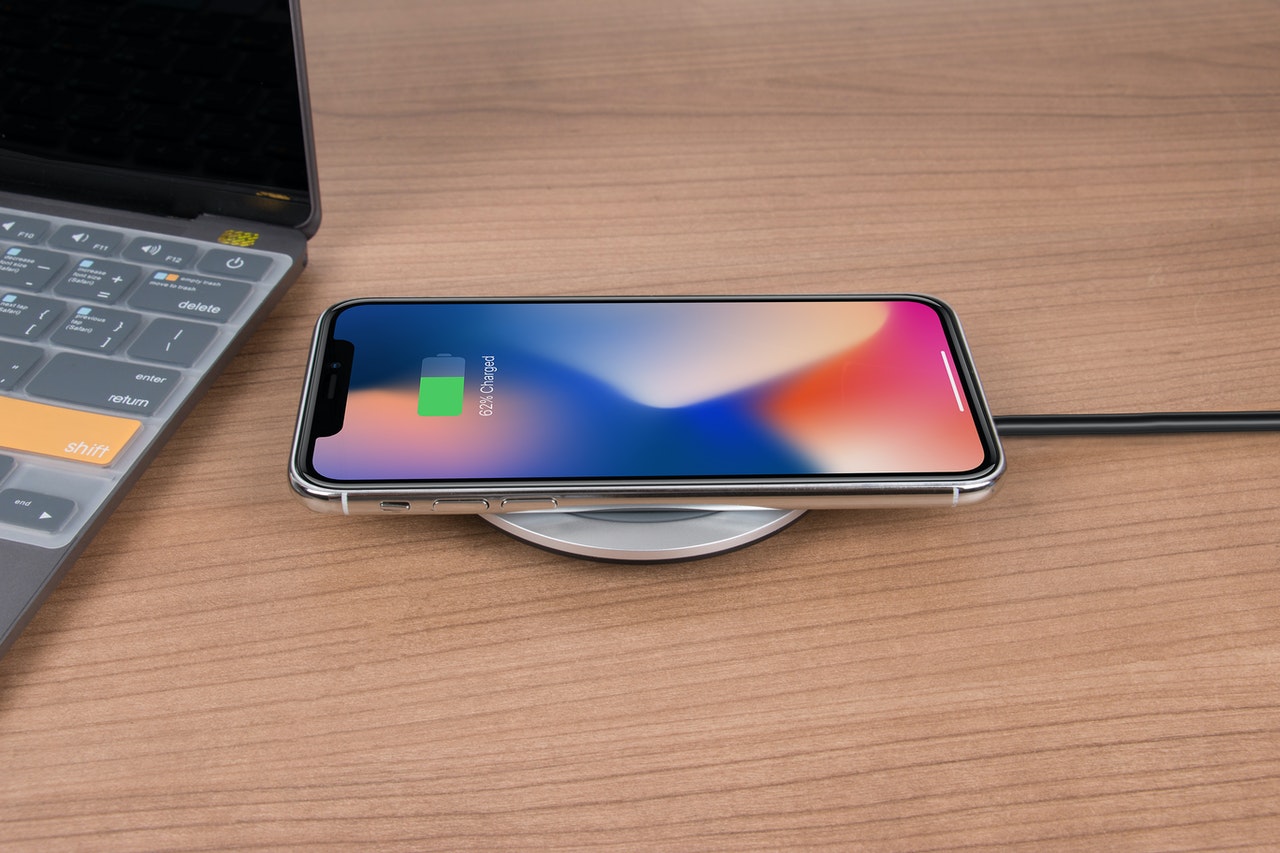
This is an ordinary coil of wire in a rigid case made of glass or a special polymer. It looks like a thin plate on which you need to put a smartphone, smartwatch, or fitness bracelet. Strictly speaking, it is not 100% wireless, since the base where gadgets are charged still needs to be supplied with current from an ordinary charging unit.
Principle of operation and technical device
Non-contact energy transfer seems like magic, but in reality, it is just a transfer of charge between two induction coils made of copper wire. One of them is located on the back of the smartphone, the other is directly in the charging base.
The principle of operation is very simple: an alternating current is supplied to the induction coil in charging, which generates a vortex electromagnetic field. It is this field that is captured by the receiver coil of the gadget that we need to charge. Then the current passes through the rectifier, is converted from AC to DC, and charges the battery of the device.
Interesting:
- Metal interferes with contactless charging, as it “suppresses” the magnetic field. Therefore, the cases of smartphones that support this standard are made of tempered glass.
- There can be many coils in the charging pad. Then you do not have to select the exact seat for the electronics so that it is charged;
- The Qi standard, in addition to the electromagnetic field, transmits data using a unique protocol that operates at a speed of 2 kbps. Thanks to this data channel, you can see information about the required time to fill the battery, a signal about the completion of charging.
Which devices use wireless charging?
With the growth of the mobile device market, there has also been interesting in wireless power transmission. This was done by the technical consortia Wireless Power Consortium and AirFuel Alliance. They stood at the origin of the main wireless charging standard – Qi (read as “Qi”). There are other, less common contactless charging standards, such as PMA, which are used by some smartphone manufacturers.
When choosing wireless charging, you need to make sure that its transmission standard is supported by your gadgets. It is this, and not the brand or model, that is the key to compatibility.
Contactless energy transfer is currently limited in power, therefore, it is used to charge small gadgets:
- smartphones;
- smartwatch;
- fitness trackers;
- electric toothbrushes.
Pros and cons of wireless charging
Advantages:
- simplicity. It is enough to put the gadget on the charging surface;
- compatibility. There is no need to select a connector, cable. Simply select the desired charging standard, any manufacturer, any brand;
- wear of connectors, plugs due to their absence are excluded.
How does contactless charging affect human health?
Short answer: no way. Naturally, it will be difficult for adherents of the world government and ardent opponents of 5G networks to believe this. Therefore, for the incredulous, we will explain.
Here are some logical reasons why wireless charging is safe:
- low frequencies of interaction. The charge transfer takes place at low frequencies (they are also called non-ionizing), which are not able to have any effect on the human body;
- when there is no gadget on the charging pad, the electromagnetic field does not spread. No charging – no harm;
- Qi 1.1 provides additional security, charging is only possible when using compatible devices that work according to this standard. That is, the platform will not charge your hand.
Results: Forward to the future or life without wires.
To talk about the future of wireless charging and contactless energy transfer in general, it is worth raising a few questions. What does IKEA have to do with this technology? Yes, the most immediate, they want to embed such chargers directly into the furniture. Put your iPhone 11 on the kitchen table or sofa rail while it charges.